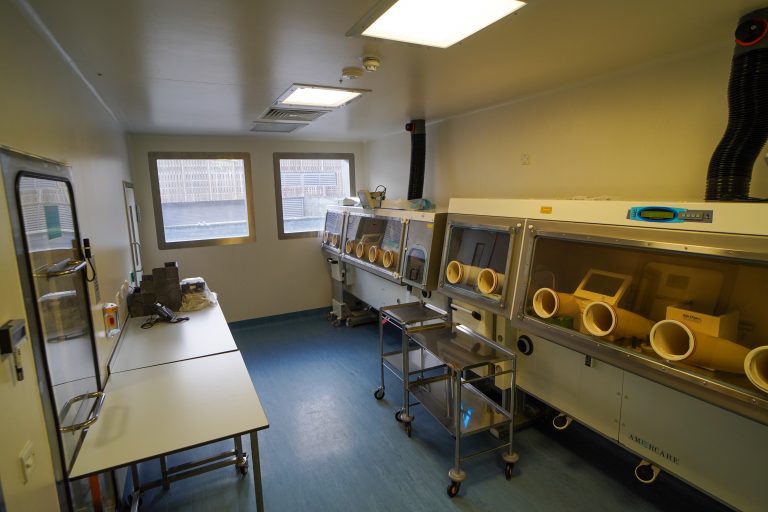
The amendments stipulated in the new Annex 1 requirements will manifest in several practical changes within cleanrooms, especially those involved in the manufacture of sterile medicinal products. Here are some real-world examples of how these changes might take shape:
Implementation of a Contamination Control Strategy (CCS):
Cleanrooms will now have a structured Contamination Control Strategy in place. This could involve new protocols for monitoring and managing microbial and particulate contamination, enhanced cleaning and sanitisation procedures, and the implementation of new or upgraded contamination control technologies.
Enhanced Quality Systems:
The quality systems within cleanrooms will likely see enhancements to align with the new Annex 1 requirements. This might include updating Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), training programs for personnel, and the implementation of more rigorous quality control and assurance processes.
Sterilisation of Lyophilizers:
In cleanrooms where lyophilization (freeze-drying) is a part of the process, the new requirement for sterilising lyophilizers before each load, especially those manually loaded or unloaded with no barrier technology separation, will necessitate changes in operational protocols. This could also potentially lead to the installation of new sterilisation equipment or technologies.
Risk Management Integration:
The shift towards a more risk-based approach will likely result in the integration of risk management principles and methodologies within the cleanroom operations. This could involve conducting risk assessments to identify potential contamination sources, and implementing measures to mitigate these risks.
Technological Upgrades:
The emphasis on real-time monitoring and control might drive cleanrooms to invest in advanced monitoring systems that provide real-time data on critical environmental parameters. This could lead to the installation of new monitoring equipment and potentially the integration of digital technologies for data analytics and reporting.
Personnel Training and Education:
With the new requirements in place, there will likely be an increased emphasis on training and educating personnel on the updated compliance standards and operational protocols. This could manifest in more comprehensive training programs and perhaps the utilisation of digital training platforms.
Documentation and Validation:
Cleanrooms will need to ensure that all processes and systems are thoroughly validated to demonstrate compliance with the new Annex 1 requirements. This might lead to a more rigorous validation process and enhanced documentation protocols.
These practical changes underscore the regulatory intent to ensure a high level of control over the cleanroom environment, promoting product sterility and safety. The transition to the new Annex 1 requirements will necessitate a collaborative effort amongst cleanroom operators, quality assurance teams, and technical personnel to ensure that all aspects of cleanroom design, operation, and maintenance align with the updated regulatory standards.